Table of Contents
Understanding how gluten affects your body is crucial, especially if you’re sensitive or intolerant. This article will give you the most recent information about gluten, regardless of whether you have celiac disease, are sensitive to it, or are just curious about its effects. It will describe how long your body will take to eliminate gluten and provide tips for healing more quickly.
How long does it take for gluten to leave your system? What Takes Place If You Consume Gluten?
Before diving into how long gluten stays in your system, it’s essential to understand what happens when you eat gluten. The cereals wheat, barley, and rye all contain the protein gluten. For most people, gluten is harmless. But for people who are sensitive to gluten or have celiac disease, gluten can trigger unpleasant symptoms like bloating, stomach pain, diarrhea, and fatigue.
Celiac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity: Key Differences
It’s important to note the critical differences between celiac disease and gluten sensitivity. Gluten causes long-term damage to the small intestine by inciting the body’s defenses against it in those with celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder. Conversely, gluten sensitivity produces uncomfortable symptoms but does not result in long-term damage. If you are aware of these differences, you can better understand why the effects of gluten on your body can differ.
How Long Does It Take for Gluten to Leave Your System?
Now, let’s address the critical question: How long does it take for gluten to leave your system? The response may change according to the quantity of gluten ingested, your body’s metabolism, and whether you have celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
For People with Gluten Sensitivity
For those with gluten sensitivity, the symptoms of gluten exposure often start within hours of eating gluten. However, your body typically clears gluten from your system within a few days, usually 2 to 3 days. The immune response calms down during this time, and symptoms gradually disappear.
How long does it take for gluten to leave your system? Factors That Affect How Long Gluten Stays in Your System
The time it takes for gluten to leave your body depends on several factors. While the general timeline is two days to 2 weeks, here are some factors that can either speed up or slow down the process:
Your Immune System
If your immune system is robust, it may clear gluten from your system faster. However, if you have a weakened immune system or chronic illness, it may take longer to recover from gluten exposure.
Amount of Gluten Consumed
The more gluten you consume, the longer it may stay in your system. A small accidental bite may clear faster than eating a whole gluten-filled meal.
Metabolism
Your body’s metabolism also affects how quickly gluten is processed. If you have a fast metabolism, gluten might leave your system quicker than someone with a slower metabolism.
Diet and Hydration
Eating a healthy, balanced diet and staying well-hydrated can help your body flush out gluten. Consuming a lot of water and eating high-fiber meals can also improve the efficiency of your digestive tract.
How long does it take for gluten to leave your system? Symptoms After Gluten Exposure: What to Expect
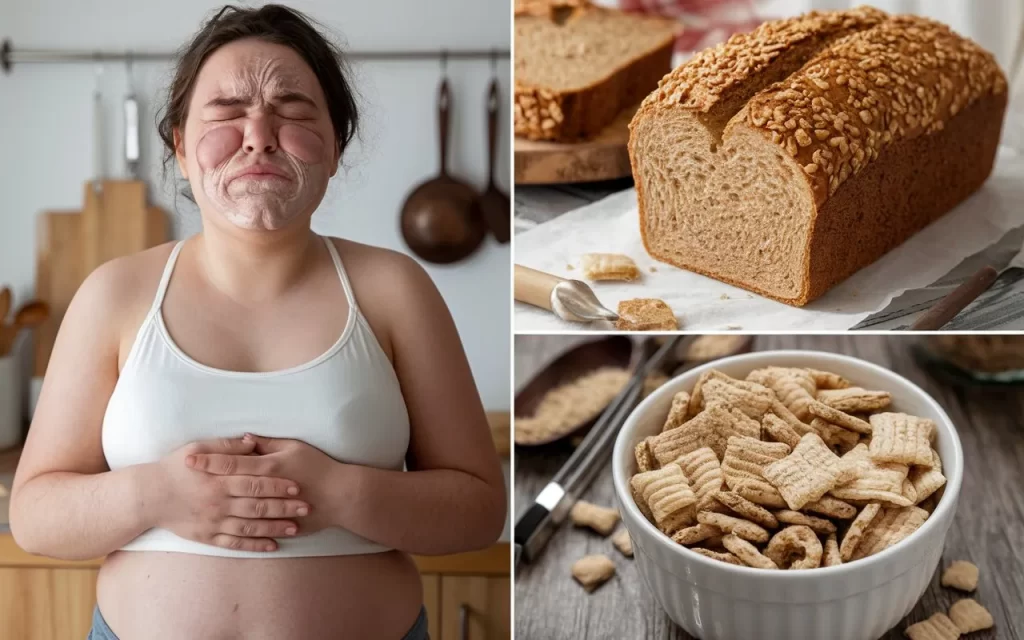

After eating gluten, people with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity may experience various symptoms. Moderate to severe variations in these symptoms depend on how much gluten was consumed and the individual’s sensitivity level.
Common Symptoms Include:
- Bloating and gas
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Stomach pain
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Joint pain
- Skin rashes
After consuming gluten, these symptoms may manifest a few hours later and may last for a few days or even weeks. See a medical practitioner if symptoms continue after this time.
How long does it take for gluten to leave your system? Tips to Speed Up Gluten Recovery?
While gluten may eventually leave your system on its own, there are several things you can do to help your body recover faster and feel better. These include staying well-hydrated, eating anti-inflammatory foods, and resting. These simple yet effective strategies can make you feel cared for and supported during recovery.
Maintain Hydration
Water consumption facilitates the removal of pollutants and can speed up the elimination of gluten from your body. To stream, drink ten glasses of water per day.
Eat to stay well-hydratedAnti-Inflammatory Foods.
Antioxidant—and anti-inflammatory-rich foods can soothe the immune response triggered by gluten. These include vegetables like leafy greens, berries, and fatty fish (like salmon).
Rest Your Body
Resting is crucial to your body’s healing process and the space it requires to mend. This is especially important if your gluten exposure causes fatigue or other severe symptoms. By prioritizing rest, you are showing care and support for your body during this time.
Probiotics for Gut Health
Probiotics can help reestablish equilibrium after gluten exposure. They support good bacteria in the digestive system, which may help quickly reduce symptoms.
Consult with Your Doctor
If you continue to experience symptoms after gluten exposure or if they worsen, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider. They may recommend medications or additional tests to assess your gut health. This step is crucial in ensuring you are on the right track to recovery, providing reassurance and confidence in your health journey.
Also Read: How Long Does Hospice Last? Heartfelt Insights Need to Know!
How long does it take for gluten to leave your system? How to Avoid Gluten Exposure in the Future
To avoid repeating gluten exposure, you must be cautious about what you eat. Because gluten can be found in many foods, it’s essential to read labels carefully. Here are some tips:
Read Food Labels
Always check ingredient labels when purchasing packaged foods. Sauces, soups, and processed snacks are unexpected places to look for gluten.
Choose Certified Gluten-Free Products
Look for products with a label stating they are gluten-free and don’t contain hidden gluten. Many brands now offer certified gluten-free bread, pasta, and snack options.
Be Cautious When Eating Out
Eating at restaurants can be risky if you’re sensitive to gluten. However, you can avoid gluten exposure by being cautious, informing your server about your dietary restrictions, and asking for gluten-free menu options. Cross-contamination in kitchens is expected, so choose restaurants specializing in gluten-free meals.
This article provides a comprehensive look at how long gluten stays in your system and practical tips to manage and speed up recovery. By following this guide, you’ll be better equipped to avoid future gluten exposure and feel your best!